Spinning the benefits of a tax cut scenario as Chancellor Jeremy Hunt hints at further tax cuts
The Chancellor, Jeremy Hunt, has given strong hints that he wants to cut taxes in the spring Budget.
Mr Hunt reportedly said that countries with lower taxes have more ‘dynamic, faster growing economies.‘ Didn’t Liz Truss say something like that too? But of course, she didn’t ‘cost it out’ in her mini budget apparently – but she also wanted lower taxes for growth none-the-less.
Autumn statement
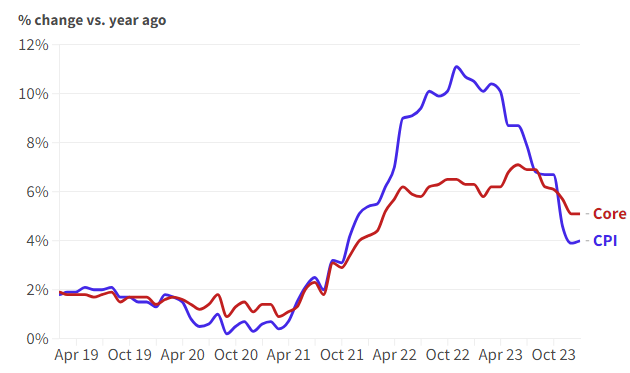
In the Autumn Statement, the chancellor reduced national insurance for workers by 2% and announced tax relief for businesses. If inflation falls, followed by lower interest rates, Mr Hunt may consider he has scope for further tax cuts.
At the World Economic Forum, in Davos, Switzerland – he was also reported to have said that the: ‘direction of travel’ indicates that economies growing faster than the UK, in North America and Asia tend to have lower taxes. ‘I believe fundamentally that low-tax economies are more dynamic, more competitive and generate more money for public services like the NHS,’ he reportedly said.
It is widely expected that the chancellor will focus on income tax in the upcoming Budget due on 6th March 2024
Lower than expected government borrowing last month has increased the possibility of tax cuts in the Budget, analysts say.
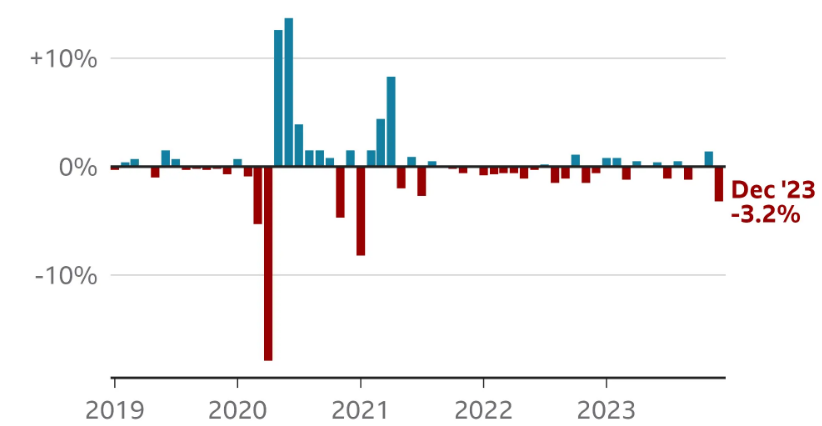
UK Borrowing fell to £7.8bn in December 2023, the Office for National Statistics (ONS) indicated. Interest payments dropped sharply due to a faster than expected decline in inflation. Analysts said the latest figures could give the chancellor more wiggle room for tax cuts.
December’s borrowing figure was £8.4bn less than a year earlier, and the lowest figure for the month since 2019.
Interest payments on government debt fell to £4bn, down by £14.1bn from December 2022.