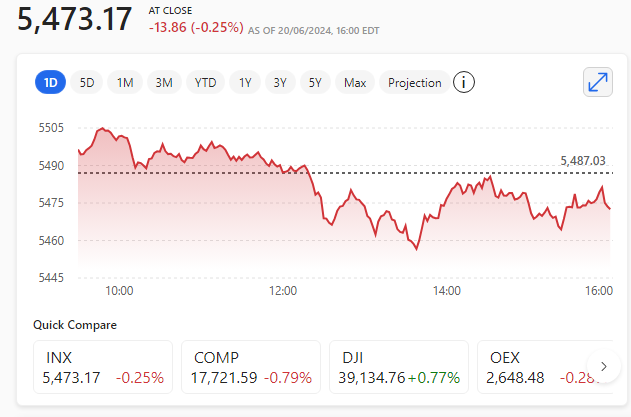
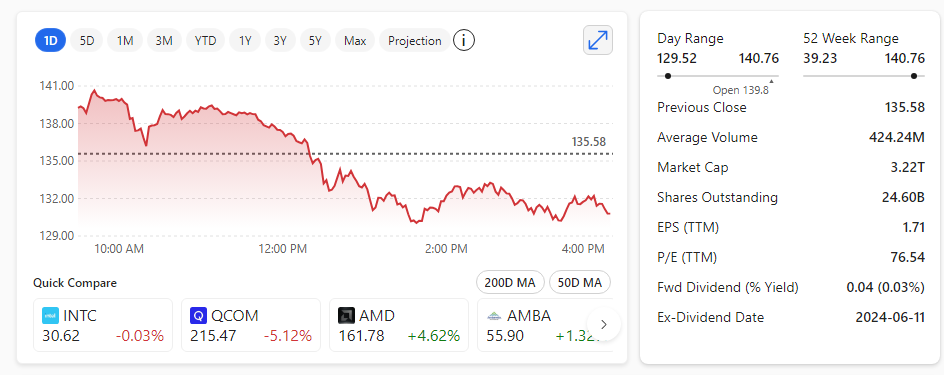
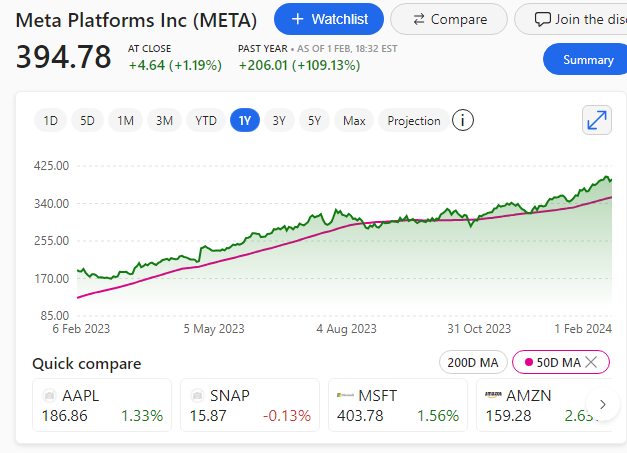
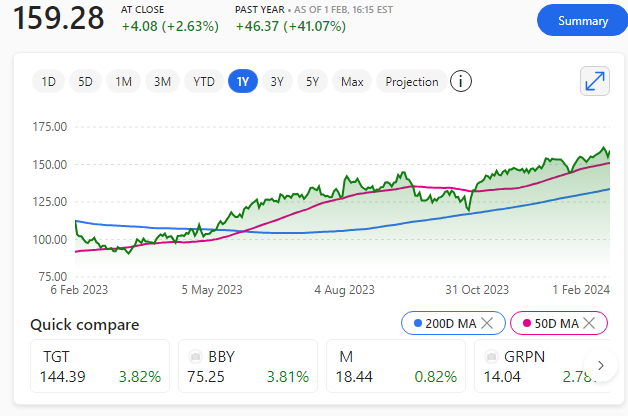
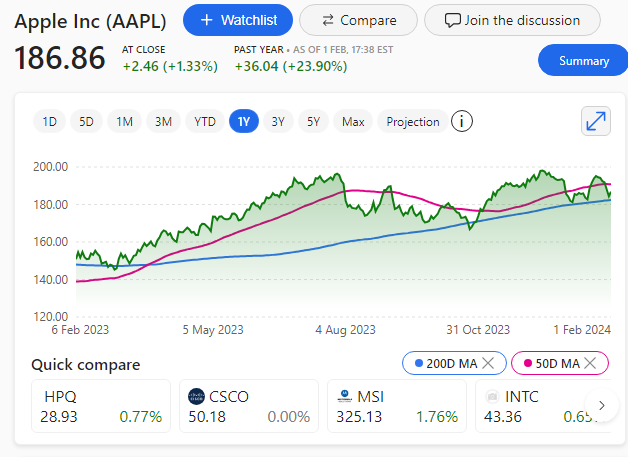
Microsoft announced on Wednesday 21st August 2024 that it will release the contentious Recall AI search feature for Windows users to test starting in October
Recall captures screenshots of on-screen activity, enabling users to search for previously seen information. Security experts raised immediate concerns about the potential risks of Windows capturing images automatically without user consent. In response, researchers developed open-source software demonstrating how attackers could easily access personal information.
Microsoft addressed these concerns in June 2024, stating that Recall would be disabled by default and promising security improvements for the feature.
While Microsoft has not provided a specific timeline for a wider release, it has introduced a new category of Windows PCs, termed Copilot+ PCs, which meet the system requirements for Recall. These PCs, produced by various manufacturers, are designed to handle AI workloads, and Microsoft has demonstrated Recall operating on these devices.
*Manufacturers are eager to demonstrate that AI models can run on local PCs, offering an alternative to cloud-based servers from companies like OpenAI. Following this trend, Apple has launched MacBooks capable of running AI models, and Microsoft’s latest Surface Pro is also a Copilot+ PC with local AI capabilities.
The timing of Recall’s broader release could be pivotal, as consumer interest in new computers may spike during the holiday season if Microsoft extends Recall to all compatible devices by that time.
*Is this a move away from AI cloud-based operations to some extent? AI tasks can easily be run in the cloud – why do we need an AI enabled device?