The International Monetary Fund (IMF) advises that the Bank of England should contemplate reducing its interest rates to 3.5% by the end of 2025.
This suggestion is made as the UK’s economy steadily recovers from the recession caused by the pandemic, while policymakers are dealing with inflationary challenges.
The ‘thinking’ behind the recommendation
Economic Recovery and Inflation Outlook
The IMF’s recommendation is grounded in its assessment of the UK’s economic trajectory.
Growth Forecast
The International Monetary Fund has upgraded its growth forecast for the UK in 2024, signaling a positive outlook. It anticipates growth of 0.7% this year and 1.5% in 2025.
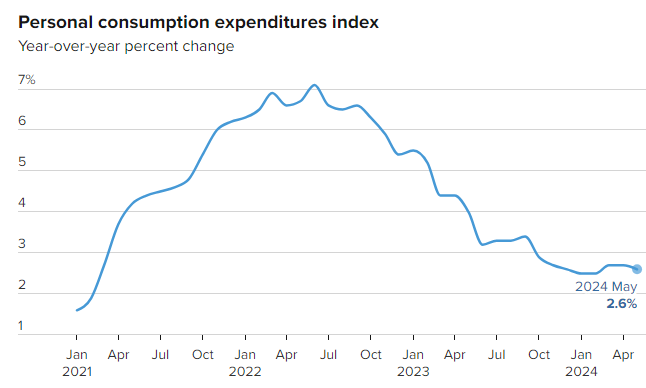
Inflation
The IMF anticipates that UK inflation will decline to near the Bank of England’s target of 2% and stabilise at this rate in early 2025, indicating that inflationary pressures are within manageable limits.
Soft Landing
The UK economy is said to be approaching a ‘soft landing‘ following the mild recession of the previous year. Policymakers are focused on finding a balance between fostering growth and managing inflation.
Monetary Policy Considerations
The Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has been closely monitoring economic indicators and inflation trends. Here’s why the IMF’s recommendation matters:
Interest Rate Peaks
The Monetary Policy Committee has indicated that interest rates might have reached their peak. The current restrictive monetary policy is having an impact on the actual economy and the dynamics of inflation.
Market Expectations
Analysts anticipate the first interest rate cut by September 2024 at the latest. Market expectations align with this projection, with the base interest rate likely to be lowered to 4% by the end of 2025.
Balancing Act
Policymakers face the delicate task of supporting economic recovery while preventing runaway inflation. The IMF’s suggestion aims to strike this balance.
Implications for Borrowers and Savers
Mortgage Holders
Variable Rate Mortgages
If you have a variable rate mortgage, a rate cut could reduce your monthly payments. However, keep an eye on your lender’s response to any rate changes.
Fixed Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate borrowers won’t immediately benefit from rate cuts, but they should still monitor the situation. If rates continue to fall, refinancing might become attractive.
Savers
Savings Accounts
Lower interest rates typically lead to diminished returns on savings accounts. It may be wise to diversify your investments to seek potentially higher yields in other areas.
Fixed-Term Deposit
Current fixed-term deposits will remain unaffected; however, new deposits might generate lower yields. It is advisable to carefully assess your alternatives.
Conclusion
The IMF’s recommendation highlights the intricate balance between fostering economic recovery and managing inflation. As the Bank of England considers its next steps, it is crucial for borrowers and savers to remain informed and adjust their financial strategies as needed.
For homeowners, investors, and savers alike, grasping the potential consequences of rate cuts is key to making well-informed choices in an ever-changing economic environment.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is based on current projections and should not be considered financial advice. It is not given as financial advice – it is for discussion and analysis only!
Consult a professional advisor for personalised recommendations.
Remember – always do your careful research first!
RESEARCH! RESEARCH! RESEARCH!
Update
The Bank of England has given its strongest hint yet that interest rates could be cut this summer. This comment was observed in a recent speech given by the deputy governor of the Bank of England.