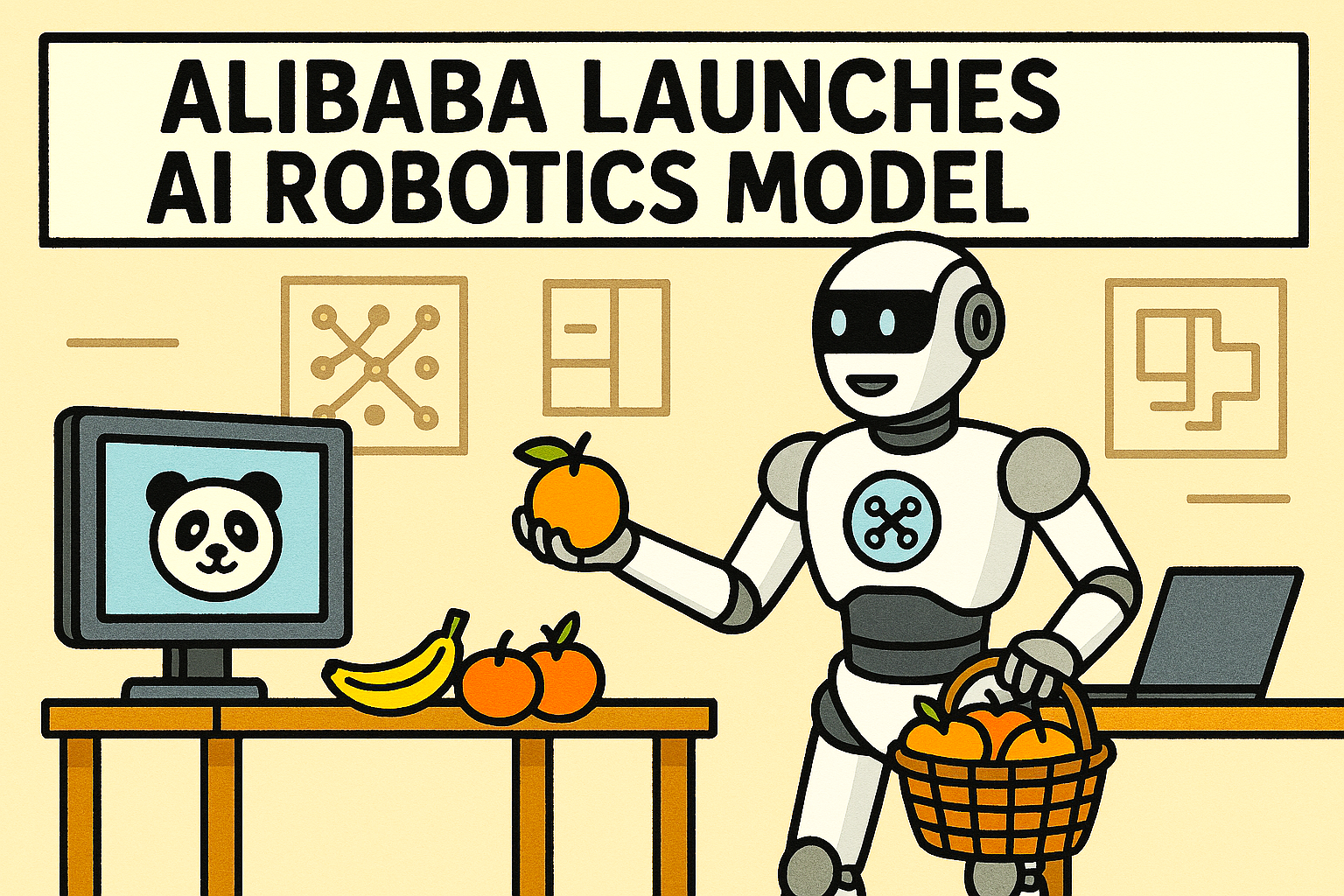
China’s Alibaba has taken a decisive step into the fast‑emerging field of ‘physical AI’ with the launch of a new foundation model designed specifically to power real‑world robots.
The model, known as RynnBrain*, marks one of the company’s most ambitious moves since restructuring its cloud and research divisions, and signals China’s intention to compete directly with the United States in embodied artificial intelligence.
Unlike traditional large language models, which operate entirely in digital environments, RynnBrain is built to interpret and act within the physical world.
It combines vision, language and spatial reasoning, enabling robots to recognise objects, understand their surroundings and plan multi‑step actions.
DAMO Acadamy
In demonstrations released by Alibaba’s DAMO Academy, the model guided a robot through tasks such as identifying fruit and sorting it into containers — a deceptively simple exercise that requires sophisticated perception and motor control.
The company describes RynnBrain as a ‘general‑purpose embodied intelligence model’, capable of supporting a wide range of robotic applications, from warehouse automation to domestic assistance.
Crucially, Alibaba has opted to open‑source the model, a strategic decision that invites global developers to build on its capabilities and accelerates the creation of a broader ecosystem around Chinese robotics research.
Physical AI
The timing is significant. Over the past year, major technology firms including Google, Nvidia and OpenAI have begun to emphasise physical AI as the next frontier of artificial intelligence.
The shift reflects a growing belief that the most transformative applications of AI will not be confined to screens, but will instead involve machines that can navigate, manipulate and collaborate within human environments.
Alibaba’s entry adds competitive pressure to a field already heating up. While U.S. companies currently dominate embodied AI research, China has made robotics a national priority, viewing it as a strategic industry with implications for manufacturing, logistics and economic resilience.
RynnBrain
By releasing RynnBrain openly, Alibaba positions itself as both a contributor to global research and a catalyst for domestic innovation.
The launch also highlights a broader trend: the convergence of AI models with physical systems. As robots become more capable and more affordable, the line between software intelligence and mechanical action is beginning to blur.
RynnBrain is an early example of this shift — a model designed not just to understand language or images, but to translate that understanding into purposeful action.
Whether Alibaba’s approach will reshape the global robotics landscape remains to be seen, but the message is clear: the race to build the brains of future machines is accelerating, and China intends to be at the forefront.
Other Major Players in Physical AI
Physical AI — AI that can perceive, reason and act in the real world — has become the next strategic battleground for global tech giants. Alibaba is far from alone.
Several companies are racing to build the ‘general‑purpose robot brain’.
Below are the most significant players.
Focus: Embodied AI, robotics‑ready multimodal model’s Key systems:
RT‑2 (Robotic Transformer)
Gemini‑based robotics extensions
Google has been working on robotics for over a decade. RT‑2 was one of the first models to show that a language model could directly control a robot arm, interpret objects, and perform multi‑step tasks.
DeepMind is now integrating robotics capabilities into the Gemini family.
Focus: General‑purpose embodied intelligence Key systems:
OpenAI Robotics (revived internally)
Vision‑language‑action research
OpenAI paused robotics in 2020 but has quietly restarted the programme. Their models are being trained to understand video, track objects and perform physical tasks. They are also working with hardware partners to test embodied versions of their models.
Focus: The infrastructure layer for physical AI Key systems:
- Nvidia Isaac (robotics platform)
- Cosmos models
- Omniverse simulation
Nvidia is not building consumer robots; it is building the entire ecosystem for everyone else. Its simulation tools, training environments and robotics‑ready AI models are becoming the backbone of the industry.
Focus: Humanoid robotics Key system:
Tesla is training its robot using the same AI stack as its autonomous driving system. The company claims Optimus will eventually perform factory and household tasks.
It is one of the most visible attempts to build a general‑purpose humanoid robot.
Focus: Warehouse automation and domestic robotics Key systems:
- Proteus (autonomous warehouse robot)
- Astro (home robot)
Amazon is integrating multimodal AI into its logistics robots and experimenting with home assistants that can navigate physical spaces.
Focus: General‑purpose humanoid robots’ Key system:
Backed by OpenAI, Microsoft and Nvidia, Figure is developing a humanoid robot designed to perform everyday tasks.
Their recent demos show robots manipulating objects and responding to natural language instructions.
In partnership with Google’s DeepMind Boston Dynamics is also building a ‘foundation model intelligence’ robot brain.
The Big Picture
Alibaba is entering a field dominated by U.S. companies, but the global race is wide open. Physical AI is becoming the next strategic platform — the equivalent of smartphones in the 2000s or cloud computing in the 2010s.
*RynnBrain explained
RynnBrain is Alibaba’s open‑source ‘physical AI‘ framework designed to give robots far more capable real‑world intelligence, enabling them to plan, navigate, and manipulate objects across dynamic environments such as factories and homes.
Developed by the company’s DAMO Academy, it competes directly with Google’s Gemini Robotics and Nvidia’s Cosmos‑Reason models, with Alibaba claiming stronger benchmark performance.
The system is released openly on platforms like GitHub and Hugging Face, offered in configurations from lightweight 2‑billion‑parameter models to advanced mixture‑of‑experts variants, and includes specialised versions—Plan, Nav, and CoP—targeting manipulation, navigation, and spatial reasoning respectively.
Its launch signals China’s ambition to lead global robotics and embodied AI development.