The short answer is no! AI hasn’t peaked in terms of potential—but the market frenzy around it may well be in bubble territory.
🚀 Signs of a Bubble?
- Valuations vs. Earnings: The top 10 companies in the S&P 500—heavily weighted toward AI giants like Nvidia, Microsoft, and Apple—are more overvalued today than during the dot-com boom.
- Retail Frenzy: Retail investors are piling into AI stocks, often driven by hype rather than fundamentals. Meme stocks and AI-branded crypto tokens are surging again.
- Low Conversion Rates: Despite massive user numbers, paid adoption is weak. OpenAI’s ChatGPT has 1.5 billion monthly users, but only 0.96% pay for it. That’s a poor monetisation ratio compared to services like Gmail. However, commercial uptake is far higher.
- Unsustainable Business Models: Many AI startups operate at huge losses, relying on speculative funding rather than sustainable revenue.
🧠 But Has AI Peaked Technologically?
No-way – not even close.
- Agentic AI: Models like GLM-4.5 from China and Anthropic’s Claude are pushing toward autonomous task decomposition—meaning smarter, more efficient systems.
- Enterprise Integration: AI is transforming workflows in law, medicine, and finance. Companies like RELX are embedding AI into decision-making tools with real-world impact.
- Hardware & Infrastructure: Microsoft and Nvidia are investing billions in AI infrastructure, suggesting long-term belief in its utility—not just hype.
What Comes Next?
- Rebalancing: Like the dot-com crash, we may see a correction. Overhyped firms could fall, while those with real utility and revenue survive and thrive.
- Regulatory Pressure: Governments are starting to scrutinise AI’s economic and ethical impact. That could reshape the landscape.
- Investor Reality Check: As soon as investors stop chasing hype and start demanding profitability, the bubble may deflate.
Less than 1% of users currently pay for ChatGPT (is this a failure to monetise or massive future potential to unfold)?
Remember how long it took Google to monetise its search engine in the beginning? Think – MySpace, Yahoo, AOL and others?
As of mid-2025, OpenAI ChatGPT has around 1.5 billion monthly users, but only a tiny fraction pay for premium plans like ChatGPT Plus ($20/month) or Pro ($200/month).
While OpenAI hasn’t published exact conversion rates, multiple industry analysts estimate that fewer than 1% of users are paying subscribers, based on app store revenue data and internal usage leaks.
This low monetisation rate is striking when compared to other freemium models:
- Gmail and Spotify convert ~5–10% of users to paid tiers
- Even niche productivity apps often hit 2–3%
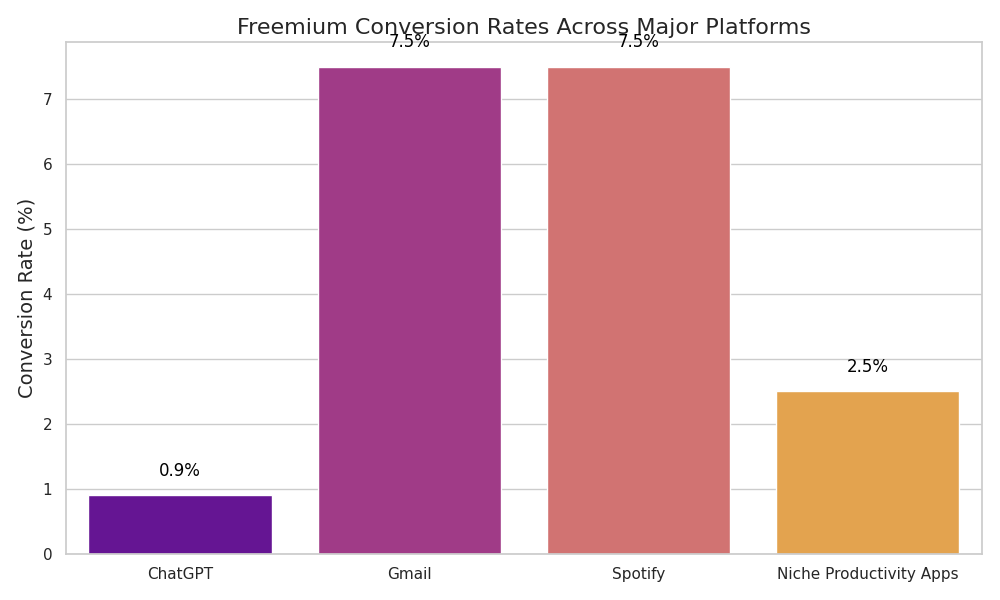
| Platform | Conversion Rate |
|---|---|
| ChatGPT | 0.9% |
| Gmail | 7.5% |
| Spotify | 7.5% |
| Niche Productivity Apps | 2.5% |
| Platform | Conversion Rate |
|---|---|
| Spotify | 7.5% |
| YouTube Music | 4.2% |
| Apple Music | 6.8% |
| Deezer | 3.9% |
| Amazon Music | 5.1% |
So, despite massive reach, ChatGPT’s revenue per user is still very low. That’s one reason why some analysts argue the AI market is in a bubble: huge valuations, but weak direct monetisation.