Albert Einstein 1879 – 1955


Google was founded 25 years ago today (4th September 2023) – by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two Stanford University students who wanted to organise the web in a better way. They named their project after the mathematical term ‘googol’, which means 1 followed by 100 zeros.
Since then, Google has grown into a global tech’ giant that offers not only search, but also email, maps, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and many other products and services.
Google has also acquired several companies, such as YouTube, Android, and Waze.

Google remains one of the most influential and innovative companies in the world. It has changed the way we access information, communicate, entertain ourselves, and solve problems. It has also inspired many people to pursue their dreams and passions.
As Google CEO Sundar Pichai wrote in his public memo on Google at 25: ‘We started with a simple mission: to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful. That mission still guides us today. But we’ve also learned that our responsibility goes beyond that. We have a duty to create products that improve the lives of billions of people — not just today or tomorrow but for generations to come’.
Go google!
Ha Jiang signed a record deal with Whet Records, Warner Music Group’s pan-Asian dance label in China, in 2021. Ha Jiang is the first virtual idol to conduct a record deal with a major label. The virtual idol uses AI technology to create music and has become an online sensation in Asia.
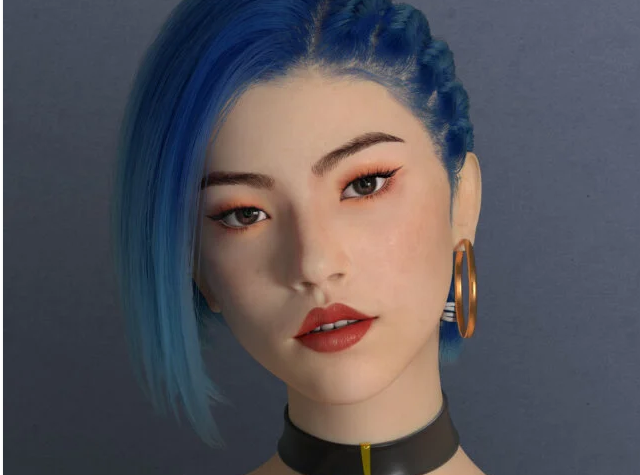

Ha Jiang is a virtual artist who uses artificial intelligence to create music. She is the first virtual idol to sign a record deal with a major label, Whet Records, which is Warner Music Group’s pan-Asian dance label in China. My understanding is that the music was composed by humans, so not entirely AI generated then.
She already has more than 100,000 followers in China and is known for her sense of style and fashion. She is also a social influencer who has been hired by the city of Shanghai to promote safe driving. Ha Jiang is not a real person, but a computer-generated avatar who only exists online. She is part of a growing phenomenon of virtual idols in Asia, especially among Gen-Z fans.
Endel, is a sound startup company that uses artificial intelligence to create personalized audio tracks. Endel was the first to sign a record deal with Warner Music Group in 2019 to release 20 albums of ambient music.
The digital pound is a proposed new form of money that would be issued by the Bank of England and backed by the government. It would be similar to a digital banknote, enabling you to use it in-store or online to make payments.
It would not be intended to replace cash, but complement it. The digital pound is also known as digital sterling or Britcoin.
The Bank of England and HM Treasury are looking at the idea of a digital pound because they think it might offer a new way to pay, help businesses, build trust in money, and better protect the UK’s financial system. They have published a Consultation Paper, which explores the need for the digital pound and proposes a set of design choices for it. They are also engaging with businesses and communities to get their views on the digital pound.
The digital pound is not a cryptocurrency or cryptoasset. Unlike cryptocurrencies, which have volatile values, the digital pound would be issued by the Bank of England and have a stable value, just like banknotes.

£10 in digital pounds would always have the same value as a £10 banknote.
Days after India’s successful moon mission, the country is now setting its sights on the sun.
According to the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), the Aditya-L1 spacecraft will be launched from the Sriharikota Spaceport on 2nd September 2023 in a bid to study the sun and its effect on space weather.
Aditya, which refers to the sun in Hindi, is to be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrangian point 1 of the Sun-Earth system, where the sun can be observed without any obstructions, an ISRO report stated.
Lagrange points are positions in space where gravitational forces of two large masses produce ‘enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion’, according to NASA. The resulting force can be used to remain in position and reduce fuel consumption – and can be likened to ‘parking places’ for spacecraft.
The launch will mark India’s first space-based observatory to study the sun, and would offer a ‘major advantage of continuously viewing the sun without any occultation or eclipses’, the ISRO report stated.

The mission would also allow for the study of solar wind, which could potentially cause disturbances on Earth, such as disrupting communications, navigation systems and weather patterns.
India’s government had granted a $46 million budget for the mission back in 2019.
India recently became only the fourth country to land on the moon, doing so with the relatively low budget of $75 million. This was a massive achievement and one India celebrated with relish.
While a first attempt for India, other countries have successfully placed orbiters to study the sun. NASA’s Parker Solar Probe in 2021 which was sent to the sun’s corona to sample particles and magnetic fields, as well as the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter which was launched the year before.
See India’s moon mission article here
Much of the UK will have no train services on Friday 1st Septemebr 2023 as the latest major strike action takes place.
Members of Aslef, the train drivers’ union, who work at more than a dozen train companies, have walked out and have refused to work.
Up to 20,000 RMT union members at 14 operators will also strike on Saturday in a long-running dispute
Meanwhile, a consultation closing most ticket offices in England ends.
Unions and disability groups have also taken action against other proposed working practices in the industry, such as ticket office closures.
Currently, nearly 300 stations in England run by train companies with Department for Transport contracts have a full-time staffed ticket office – 708 are staffed part-time. Under the proposals, most would close.

The UK train strikes are part of an ongoing dispute between the rail unions and the train operators over pay and conditions.

The rail unions are demanding a pay rise that reflects the rising cost of living, as well as job security and improved working conditions. The train operators say they need to make changes to the ways of working in order to save money and improve efficiency, especially after the pandemic hit their finances hard.
The Rail Delivery Group, which represents the train operators, has offered a 5% pay rise for 2022, but the unions have rejected it as insufficient and conditional on reforms they oppose.
The train strikes have caused significant disruption and frustration for millions of passengers, especially during the peak summer holiday season. The government has urged both sides to resume talks and find a resolution

Nationwide said the drop represented a fall of £14,600 on a typical home in the UK since house prices peaked in August 2022. It also said higher borrowing costs for buyers had led to a slowdown in activity in the housing market. Mortgage approvals are also about 20% below pre-Covid levels.
Since December 2021, the Bank of England (BoE) has raised interest rates 14 times in row in a bid to clamp down on rising inflation in the UK. The bank’s base rate now stands at 5.25%. This has led to lenders raising their mortgage rates, putting increased pressure on homebuyers.
The average two-year fixed mortgage rate on Friday was 6.7%, while the average five-year fix was 6.19%.
Average house prices in the UK peaked at £273,751 in August 2022 but fell to £259,153 last month.
They are all big commercial markets but in the coming decades a new product is coming and it will be so desirable that it will dwarf these giants – it will be… the ‘robot’.
Robots will be able to understand what we want, comprehend the way the world works and looks and have the skills to execute our commands in a safe and controlled manner – at home and in the workplace.
The labour market is the biggest market that has ever existed in the history of business – it’s the market where we want things ‘done’ – where we do things – and it’s forever evolving. It carries massive stock market and investing potential right now and for the future.
Take Nvidia, Microsoft, Google, Meta, Apple and Tesla as prime examples of companies pioneering technological advancements for instance – we can already enjoy and invest in these – and there’s much more to come.
In the UK, Dyson is investing in AI and robotics aimed at household chores.
One of the highest profile companies in the market is Tesla, Elon Musk’s electric car company. It is working on the Optimus humanoid robot, which Mr Musk intimates could be on sale to the public in a few years’ time.
Massive tecnological advancement in artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics suggest the development of humanoid robots is accelerating… and fast. It’s a race to the become the first to succeed in the biggest practical labour market ever… and it carries huge potential for everyone, including you and me.
Twenty years at the pace the technology is developing now is is an eternity – every week, month and year there are new developments in the AI world that have introduced fundamental changes and enhancements to our world.
Mainstream interest in AI exploded late 2022 when a powerful version of ChatGPT was made public. Its ability to generate almost unlimited useful text and images has spawned rivals and a wave of investment in AI technology.
But developing the AI that would allow a robot to complete useful tasks is a different and much more difficult task. Tesla could be the company best placed to be one of the first to achieve this goal – given its advancements in ‘self driving’ technology. But, unlike ChatGPT and its rivals, humanoid robots have to navigate the physical world and need to understand how objects in that world relate to each other.
Tasks that seem easy to humans are major feats for humanoid robots. This is a problem that engages a lot of different complex issues in an AI driven robotics system. Picking up a cup and having a drink is a major undergoing for a robot.
The potential market for robots in the future depends on various factors, such as the level of technological innovation, the demand from different industries and sectors, the regulatory and ethical frameworks, and the social and economic impacts of robot adoption. But if recent developments are anything to go by – it promises to be big!
Based on the some indicative web search results, the current market size for robots is estimated to be around $55 billion to $114 billion in 2023, depending on the type and scope of robots included. The projected market size for robots in 2028 or 2029 ranges from $165 billion to $260 billion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% to 17.6%.
The professional services robots, which include medical, agricultural, and personal assistance robots, are expected to dominate the market and account for more than half of the total sales by 2030. The industrial and logistics robots, which include conventional, collaborative, and mobile robots, are also expected to grow steadily and increase their productivity and efficiency in various manufacturing and transportation applications.
However, these projections are based on assumptions – but one thing is for sure the robots are coming and the market will be massive!
I for one will be keeping a watchful eye on where to invest my hard earned cash to take advantage of this potentially high growth market in the coming years (and now).
Nvidia stock anyone?
At 4.33%, the 10-year Treasury yield in the U.S. is at its highest in 16 years. That represents a risk-free, long-duration asset with relatively high returns and this is challenging the stock market.
Why should traders invest in stocks that may not return as much, or just slightly more and take unecessary risks, when there is an asset class that guarantees around 4% return or slighlty more?
Cash is now yielding 5% in the U.S., short term bonds are yielding 5% plus, so equities for the first time in a long time, have actually got some competition.
Typically stocks if they do well, are likely to return more than a risk-free asset, precisely because it isn’t certain stocks will rise. That’s called the equity risk premium, a return that’s supposed to compensate stock investors for the chance that they might lose money. But, as the premium is below 1% now. Historically, it’s been between 2% and 4% – meaning stocks are looking much less attractive than Treasuries.
Another potential issue that could crop up with high Treasury yields is that it could make the Federal Reserve’s job tougher. During the recent Jackson Hole gathering, the Fed head has indicated that more interest rate hikes are still high possibility.
But don’t panic just yet… this is likely a pullback phase of a bull market analysts suggest. That is, it’s still too early to be bearish on stocks.
Yardeni Research president Ed Yardeni is reported to have said that the market is ‘going to hang in there’ and ‘a year-end rally will bring the S&P 500 back to something like 4,600‘.
That implied an increase of almost 5% in stocks – while not certain – would give Treasuries a run for their money again.
Holidaymakers are stuck all over the UK and abroad, with the National Air Traffic Services (NATS) saying it had applied restrictions to traffic flow. Passengers have been advised to check if their flight has been affected on one of the biggest UK travel days of the year.
NATS reportedly apologised for the fault just after midday on bank holiday Monday 28th August 2023, before it announced at 15:15 BST that it had identified and remedied the issue that was affecting its ‘ability to automatically process flight plans’. We don’t yet know what caused the failure. NATS added that engineers would be monitoring the system’s performance as it returns to normal.
NATS had earlier stressed that ‘UK airspace was not closed, we have had to apply air traffic flow restrictions which ensures we can maintain safety’.
Several airports across the UK, and most airlines have all warned passengers of delays or cancellations to flights.
How fragile are the infrastructures systems in the UK?

This is a controversial decision that has been opposed by China, South Korea, and some Pacific island nations. They fear that the water release will harm the marine environment and human health, and affect seafood exports.
Japan says that the water release is safe and necessary for the decommissioning of the plant, which was damaged by a massive earthquake and tsunami in 2011. The water has been treated to remove most of the radioactive substances, except for tritium and carbon-14, which are considered to have low risks. The water will also be diluted to meet the international standards for drinking water before being discharged.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has endorsed Japan’s plan and said that the water release will have a negligible impact on people and the environment. The IAEA will also monitor the water release and verify Japan’s compliance with the safety standards.
The water release is expected to take about 30 years to complete, and will involve pumping out about 1.34 million tonnes of water from more than 1,000 tanks at the Fukushima site.

The former boss of NatWest is set to receive a £2.4m pay package this year, despite having quit in disgrace over her handling of the closure of Nigel Farage’s bank account.
A contractual obligation no doubt?


ChatGPT, the popular artificial intelligence chatbot, shows a significant and systemic left-wing bias, UK researchers have found. According to the new study by the University of East Anglia, this includes favouring the Labour Party and President Joe Biden’s Democrats in the U.S.
Concerns about an inbuilt political bias in ChatGPT have been raised before, notably by SpaceX and Tesla tycoon Elon Musk, but the academics said their work was the first large-scale study to find proof of any favouritism.
Lead author o the report reportedly warned that given the increasing use of OpenAI’s platform by the public, the findings could have implications for upcoming elections on both sides of the Atlantic. Any bias in a platform like this is a concern’, he said. If the bias were to the right, we should be equally concerned.
Sometimes people forget these AI models are just machines. They provide very believable, digested summaries of what you are asking, even if they’re completely wrong. And if you ask it ‘are you neutral’, it says ‘oh I am!’ Just as the media, the internet, and social media can influence the public, this could be very harmful. I have personally witnessed incorrect responses from ChatGPT where the AI ‘system’ 100% believed ‘it’ was correct and would not engage in a debate as ‘it’ was right!
The chatbot, which generates responses to prompts typed in by the user, was asked to impersonate people from across the political spectrum while answering dozens of ideological questions. These questions ranged from radical to neutral, with each ‘individual’ asked whether they agreed, strongly agreed, disagreed, or strongly disagreed with a given statement.
Its replies were compared to the default answers it gave to the same set of queries, allowing the researchers to compare how much they were associated with a particular political stance.
Each of the more than 60 questions was asked 100 times to allow for the potential randomness of the AI, and these multiple responses were analysed further for signs of bias.
Dr Motoki described it as a way of trying to simulate a survey of a real human population, whose answers may also differ depending on when they’re asked.
Bias was descovered in the Chatbot repsonses.
The Cambridge-based company, which designs chips for devices from smartphones to game consoles, plans to list on New York’s Nasdaq in September. The highly anticipated IPO in the U.S. comes after UK Prime Minister, failed to convince Arm to float in London or pursue a dual UK-U.S. listing.
Arm’s decision to list in New York rather than London has fuelled fears that the City is losing its competitiveness to Wall Street, where valuations are typically higher. SoftBank-owned chip designer Arm on 21st August 2023 disclosed a modest 1% fall in annual revenue as it made public the paperwork for a U.S. listing that is expected to be the year’s biggest initial public offering. The company is reportedly looking for a valuation of between $60bn (£47bn) to $70bn.
Arm was bought in 2016 by Japanese conglomerate Softbank in a deal worth £23.4bn. Prior to the takeover, it was listed in both London and New York for 18 years.
Some of the companies that use ARM processors include Apple, Qualcomm, Samsung, Broadcom, and Fujitsu. ARM technology is used in a wide range of devices, from smartphones to game consoles to supercomputers.
Arm is a British semiconductor and software design company that is known for its Arm processors, which are widely used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other devices. Arm was founded in 1990 as a joint venture between Acorn Computers, Apple Computer, and VLSI Technology. The company was originally called Advanced RISC Machines, but later changed its name to Arm Ltd in 1998.
The NRR is an assessment of the risks facing the UK that would have a significant impact on the UK’s safety, security or critical systems at a national level. The NRR is based on the government’s internal, classified risk assessment and offers more detail on the potential scenarios, response and recovery options relating to the risks.
The 89 threats are divided into four categories: natural hazards, malicious attacks, accidents and system failures, and global events.

The NRR also provides information on how likely each threat is to occur in the next five years (from very low to very high), how severe the impact would be on the UK (from minor to catastrophic), and what actions the government and other stakeholders are taking to prevent or mitigate the risks.
The NRR is intended to help the public and businesses better understand and prepare for potential threats facing the country now and in the future.
The U.S. stock market has experienced a 5.6% slide for the S&P 500 index over 15 trading sessions through 17th August 2023 and levelling off in the last trading day of that week.
This is about as bad as August typically gets, as August is a rocky month with low volume and high volatility. Some of the reasons for the pullback include the rise in the 10-year Treasury yield, the strengthening of the U.S. dollar, and the signs of a slowing Chinese economy.
However, some analysts argue that the pullback will likely prove to be temporary and not turn into a serious market rout. It has been suggested that the bull run isn’t quite over just yet, and that a 10% ‘pullback’ was on the cards.
Analysts also suggest that the rise in yields would need to threaten a serious shift or there would need to be an additional shock to cause a larger selloff.

However, some suggest that the market is showing signs of stability, as the speed of the surge in the 10-year yield often occurs near the end of a selling cycle for equities. Investors should watch for indicators such as oil prices, wage pressures, and inflation expectations to gauge the market sentiment.
The S&P 500 and the Dow levelled off the week at the close of trading Friday 18th August 2023.
The NASDAQ did score its best first half of the trading year since 1983 January to June 2023 so a pullback was likely to happen.
A new artificial intelligence (AI) road safety camera system has been deployed on the A30 near Launceston, Cornwall, by Devon and Cornwall Police.
The camera system uses AI to detect potential offences such as using mobile phones or not wearing seatbelts while driving. The camera system can capture ultra clear images of the car’s interior and send them to a human reviewer who can issue a warning letter or a notice of intended prosecution, depending on the severity of the offence.
The camera system is the first of its kind to be used in the UK and it has caught almost 300 drivers breaking the law in the first three days of its operation. The camera system is part of the Vision Zero South West project, which aims to reduce road deaths and serious injuries in Devon and Cornwall. The project conducted a 15-day trial of a similar vehicle-based system last year and detected 590 seat belt and 45 mobile phone offences across various roads in the two counties.
The police hope that the new technology will help deter drivers from using their phones or not wearing their seatbelts, which are both dangerous and illegal behaviours that put people’s lives at risk.
The road safety system is from tech’ firm Acusensus.
The police have reportedly said they are ‘disappointed’ by the number of people not wearing seatbelts orand using their mobile ‘phones when drving.
This quote is from ‘Lady Windermere’s Fan’.

Singapore’s financial regulator has reportedly said it had finalised rules for a type of digital currency called ‘stablecoin’, placing it among some of first the regulators worldwide to do so.
Stablecoins are a type of digital currency designed to hold a constant value against a fiat currency. Many claim to be backed by a reserve of real-world assets, such as cash or government bonds.
Reserves that back stabelcoins must be held in low-risk and highly-liquid assets. They must equal or exceed the value of the stablecoin in circulation at all times, the rules say. The stablecoin market is valued at around $125 billion, with two tokens – Tether’s USDT and Circle’s USDC – dominating roughly 90% of the market cap value. Stablecoins are broadly unregulated around the world.
These rules will apply to stablecoins that are issued in Singapore and mimic the value of the Singapore dollar, or of any G10 currencies, such as the U.S. dollar.

Last year, the collapse of a so-called algorithmic stablecoin named UST put this type of stablecoin in the crosshairs of regulators. Unlike USDT and USDC, UST was governed by an algorithm and did not have real-world assets like bonds in its reserves.
Singapore’s stablecoin framework puts it among one of the first jurisdictions to have such rules. In June, the U.K. passed a law that gives regulators the ability to oversee stablecoins, though there are no concrete rules yet. Hong Kong is meanwhile undergoing a public consultation on stablecoins and seeks to introduce regulation next year.
A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency that tries to maintain a stable value by being pegged to another asset, such as a fiat currency, a commodity, or another cryptocurrency. Stablecoins aim to offer the benefits of cryptocurrencies, such as decentralisation, security, and transparency, without the drawbacks of high volatility and price fluctuations.
Stablecoins can be used for payments, remittances, trading, and storing value. However, stablecoins also face some challenges and risks, such as regulatory uncertainty, technical issues, and trust issues.
There are different ways to create and manage stablecoins, depending on the mechanism used to stabilize their value.
Crypto has attracted a lot of attention in recent years. Crypto is short for cryptocurrency, which is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography to secure and verify transactions. Crypto can also refer to the underlying technology that powers cryptocurrencies, such as blockchain.
Some examples of popular cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple ( XRP)and Cardano (ADA).

Cryptocurrencies have many advantages over traditional currencies, such as decentralisation, transparency, anonymity, and lower fees. However, they also face some challenges, such as volatility, regulation, security, and scalability. Crypto enthusiasts believe that cryptocurrencies have the potential to revolutionise the world of finance and beyond.
Some examples of popular stablecoins are Tether, USD Coin and Binance USD.
Asia is promoting clear crypto rules at a time when large businesses are facing regulatory uncertainty in the U.S.
Some Asian countries that have taken the lead in crypto regulation include Singapore, Hong Kong, Japan, and South Korea. They have proposed or implemented frameworks that protect investors, prevent money laundering, and encourage innovation in the crypto industry.
In contrast, the U.S. has been singled out for its lack of clarity and consistency in crypto regulation. The SEC for instance and other agencies have different views on how to classify and regulate crypto assets – take alook at the case with XRP and ripple of recent years.
Some industry leaders have threatened to leave the U.S. or sued the regulators over their actions. There is also a debate in Congress that could level crypto transactions with a tax.
As a result, some analysts have suggested that Asia could become more attractive to investors and innovators in the crypto industry, as it offers more certainty and stability in the regulatory environment.
However, there are also challenges and risks involved in crypto regulation, such as balancing security and innovation, ensuring compliance and enforcement, and dealing with cross-border issue.
Welcome to the birth of digtal currency.
The glitch reportedly also added €1,000 to some accounts without explanation. This led to large crowds forming at ATMs across the country, hoping to take advantage of the error.
Some reports suggest that the police were called to calm some situations as some ATMs ran out of cash. The bank has since fixed the problem and warned customers that any excess money they withdrew or transferred will be debited from their accounts.
The bank also apologized for the disruption and urged customers who may face financial difficulties due to overdrawing on their accounts to contact them.
Questions remain – how or even why did this happen?

Wages grew at a record annual pace between April and June 2023, according to new figures from the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
Regular pay grew by 7.8%, the highest annual growth rate since comparable records began in 2001.Inflation, which measures the pace at which prices are rising, has eased but remains relatively high at 7.9%. Thhe ONS suggested these latest figures demonstrates ‘people’s real pay is recovering‘ and that basic pay is growing at its fastest since current records began’.
However, wage growth is still not quite outstripping the pace of price rises and inflation is still high. Figures suggest that, taking into account the Consumer Prices Index (CPI) measure of inflation, average regular pay fell by 0.6%.
There are signs in the ONS’s data that the UK employment market is easing. The jobless rate rose from 4% to 4.2%, while the number of people in employment ticked lower.
The fall in employment in the three months to June and the further rise in the unemployment rate will be welcomed by the Bank of England as a sign labour market conditions are cooling. These comments from an analyst were presented as welcome news – but they are odd really when an economy needs good levels of employment (not unemployment). We live in weird times! Good news! Bad news!
The Bank of England is still generally expected by many pundits to increase its key interest rate again to 5.5% before ending the current run of rate rises.
The number of vacancies in the UK jobs market fell again, down 66,000 between May and July 2023. However, there are still more than one million vacancies.
List of workers striking for higher pay
This is by no means an exhaustive list – just a sample of the demands placed on resources through strike action that impacts inflation through a period of fast wage growth.
Japan’s economy posted its third straight quarterly expansion, latest government data showed 15th August 2023, as robust export growth contributed to an annualised 6% expansion in the second quarter, easily beating market expectations.
Economists had reportedly expected the world’s third-largest economy to produce a 3.1% growth in the April-June quarter. The GDP data translated to a more modest quarterly expansion of 1.5%, topping expectations for 0.8% growth.
The strong performance was mainly driven by a surge in exports, especially in the auto sector, as global demand recovered from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Japan also benefited from an increase in inbound tourism, as travel restrictions eased and the Tokyo Olympics boosted visitor arrivals.
However, the outlook for the Japanese economy remains uncertain, as the country faces a resurgence of COVID-19 cases and a sluggish consumer recovery. The government has extended a state of emergency in several regions, including Tokyo and Osaka, until the end of August, which could dampen domestic spending and business activity.
Quarterly expansion came in at a more modest 1.5%, versus expectations for 0.8% growth.
Optimism was tempered by muted domestic demand, given a surprise drop in private consumption expenditure despite the first employee compensation sequential increase in seven quarters.
The Bank of Japan has maintained its ultra-easy monetary policy stance, keeping its key interest rate at -0.1% and pledging to support the economy with massive asset purchases.
The central bank has also introduced a new lending scheme to encourage green and digital investment for the future.
Russia’s central bank has announced a surprise hike in its key lending rate by 3.5%, from 8.5% to 12%, as the country’s economic recovery loses steam amid a resurgence of COVID-19 cases and weak domestic demand.
The decision was announced after an emergency meeting of the bank’s board of directors was called a day earlier as the ruble declined. The fall comes as Moscow increases military spending and Western sanctions weigh on its energy exports.
The Russian currency passed 101 roubles to the dollar on Monday, losing more than a third of its value since the beginning of the year and hitting the lowest level in almost 17 months. It had recovered slightly after the central bank announced the meeting.
The central bank blamed the weak ruble on ‘loose monetary policy‘, suggesting that bank has ‘all the tools necessary‘ to stabilize the situation.
By raising borrowing costs, the central bank is trying to fight price spikes as Russia imports more and exports less, especially oil and natural gas, with defense spending going up and sanctions taking a toll. Importing more and exporting less means a smaller trade surplus, which typically weighs on a country’s currency.
The bank also made a big rate hike of 1% last month, saying inflation is expected to keep rising and the fall in the ruble is adding to the risk.
After Western countries imposed sanctions on Russia over the invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the ruble plunged to a low of 130 to the dollar, but the central bank enacted capital controls that stabilized its value.
The Voyager 2 spacecraft is a remarkable feat of human exploration and discovery. It was launched in 1977, along with its twin Voyager 1, to explore the outer planets of our solar system. It is the only spacecraft to have visited Uranus and Neptune, and it is now the second most distant human-made object in space, after Voyager 1.
However, communicating with such a faraway spacecraft is not easy. It requires a powerful radio antenna that can send and receive signals across billions of miles. NASA uses its Deep Space Network (DSN), a network of giant radio dishes around the world, to keep in touch with Voyager 2 and other deep space missions.
Unfortunately, sometimes things can go wrong. On July 21, 2023, NASA accidentally sent a wrong command to Voyager 2 that caused it to tilt its antenna away from Earth. This meant that the spacecraft could not receive any more commands or send back any data. NASA lost contact with Voyager 2 for nearly two weeks.
But NASA did not give up. The engineers tried to send a corrective command to Voyager 2 using the DSN, hoping that the spacecraft would somehow pick it up and respond.

On August 1, 2023, NASA finally received a signal from Voyager 2. It was a faint ‘heartbeat‘ that confirmed that the spacecraft was still alive and broadcasting. NASA was overjoyed and relieved to hear from its old friend.
On August 4, 2023, NASA announced that it had successfully restored full contact with Voyager 2. The engineers had managed to send an ‘interstellar shout’ to the spacecraft, a powerful command that instructed it to point its antenna back to Earth. It took 37 hours for the command to reach Voyager 2 and another 37 hours for the confirmation to come back. It worked! Voyager 2 was back online and ready to resume its mission.
Voyager 2 is an amazing example of human ingenuity and perseverance. It has been exploring space for nearly half a century, and it is still going strong. It has taught us so much about our solar system and beyond, and it continues to send us valuable data from the interstellar space. We are lucky to have such a faithful companion in our cosmic journey
Voyager 1 is an amazing spacecraft that has been exploring the outer solar system and beyond for over 45 years. It is currently the most distant human-made object from Earth, and it is still sending us valuable data from interstellar space.
According to the latest information from NASA, as of April 7, 2023, Voyager 1 is about 14,803,648,909 miles (23,837,577,852 kilometers) away from Earth. That is equivalent to 160.154936 astronomical units (AU), which is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun.
To put that in perspective, it would take light about 22 hours and 4 minutes to travel from Voyager 1 to Earth. That means that we are receiving signals from Voyager 1 that were sent almost a day ago! It takes approximately 8 minutes for light to travel from the Sun to planet Earth
Voyager 1 is also moving away from Earth at a speed of about 38,026.77 miles per hour (or 61,198.15 kilometers per hour) relative to the Sun. That means that it is getting farther and farther away from us every second. At this rate, it will take Voyager 1 about 40,000 years to reach the nearest star system to our Sun, which is Alpha Centauri.

Voyager 1 is a testament to human curiosity and ingenuity. It has taught us so much about our solar system and beyond, and it continues to inspire us to explore the unknown.
Nice one Voyager 1
NASA’s StarChild: This is a website that offers information and activities for children about stars and other astronomical topics.
Stellarium: This is a free software that simulates the sky in 3D and allows you to explore the stars and constellations from any location and time.
StarDate: This is a website that provides daily updates on the sky events, such as star sightings, eclipses, meteor showers, and planetary alignments.
The Electoral Commission said unspecified ‘hostile actors‘ had managed to gain access to copies of the electoral registers, from August 2021. Note the word ‘unspecified’ is used – do they even know?
Hackers also broke into its emails and “control systems” but the attack was not discovered until October last year. The watchdog has warned people to watch out for unauthorised use of their data.
The commission said hackers accessed copies of the registers it was holding for research purposes, and for conducting checks on political donors. The commission knew which of its systems were accessible to the hackers, but could not ‘conclusively‘ identify which files may have been accessed.
The personal data held on the registers – name and address – did not itself present a ‘high risk‘ to individuals, it added, although it is possible it could be combined with other public information to ‘identify and profile individuals’.
It has not said when the hackers’ access to its systems was stopped, but said they were secured as soon as possible after the attack was identified in October 2022. Why was it left so long to be made public and how long did it take to make systems secure again?
Explaining why it had not made the attack public before now, the commission said it first needed to stop the hackers’ access, examine the extent of the incident and put additional security measures in place.Defending the delay, commission chair John Pullinger said: “If you go public on a vulnerability before you have sealed it off, then you are risking more vulnerabilities.” He is reported to have said the ‘very sophisticated attack involved using software to try and get in and evade our systems’. Well, that clearly worked then.

He reportedly said that the hackers were not able to alter or delete any information on the electoral registers themselves, which are maintained by registration officers around the country. Information about donations and loans to political parties and registered campaigners is held in a system that is not affected by this incident, the notice added. He understood public concern, and would like to apologise to those affected.
The commission added that it had taken steps to secure its systems against future attacks, including by updating its login requirements, alert system and firewall policies. The Information Commissioner’s Office, which is responsible for data protection in the UK, said it was urgently investigating.
Labour’s deputy leader Angela Rayner reportedly said: ‘This serious incident must be fully and thoroughly investigated so lessons can be learned‘. Why wouldn’t it be investigated? I dislike it immensely when clueless politicians roll out this ‘standard remark’ as an attempt to demonstrate they ‘know what’s going on’.
Then what? It happens again and we have to… learn more lessons…?
Step up the security – we have the ability!