In the early 1970s, President Richard Nixon’s pursuit of re-election collided with the Federal Reserve’s independence, triggering a cascade of economic consequences that reshaped global finance.
The episode remains a cautionary tale about the dangers of politicising monetary policy.
At the heart of the drama was Nixon’s pressure on Fed Chair at the time, Arthur Burns to stimulate the economy ahead of the 1972 election. Oval Office tapes later revealed Nixon’s direct appeals for rate cuts and looser credit conditions—despite rising inflation.
Burns, reluctant but ultimately compliant, oversaw a period of aggressive monetary expansion. Interest rates were held artificially low, and the money supply surged.
The short-term result was a booming economy and a landslide victory for Nixon. But the longer-term consequences were severe. Inflation, already simmering, began to boil. By 1973, consumer prices were rising at an annual rate of over 6%, and the dollar was under siege in global markets.
Then came the real shock: in August 1971, Nixon unilaterally suspended the dollar’s convertibility into gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system.
This move—intended to halt speculative attacks and preserve U.S. gold reserves—unleashed a new era of floating exchange rates and fiat currency. The dollar depreciated sharply, and global markets entered a period of volatility.
By 1974, the consequences were fully visible. The Dow Jones Industrial Average had fallen nearly 45% from its 1973 peak.
Bond yields soared as investors demanded compensation for inflation risk. The U.S. economy entered a deep recession, compounded by the oil embargo and geopolitical tensions.
The Nixon-Burns episode is now widely viewed as a breach of central bank independence. It demonstrated how short-term political gains can lead to long-term economic instability.
The Fed’s credibility was damaged, and it took nearly a decade—culminating in Paul Volcker’s brutal rate hikes of the early 1980s—to restore price stability.
Today, as debates over Fed autonomy resurface, the lessons of the 1970s remain urgent. Markets thrive on trust, transparency, and institutional integrity. When those are compromised, even the most powerful economies can falter.

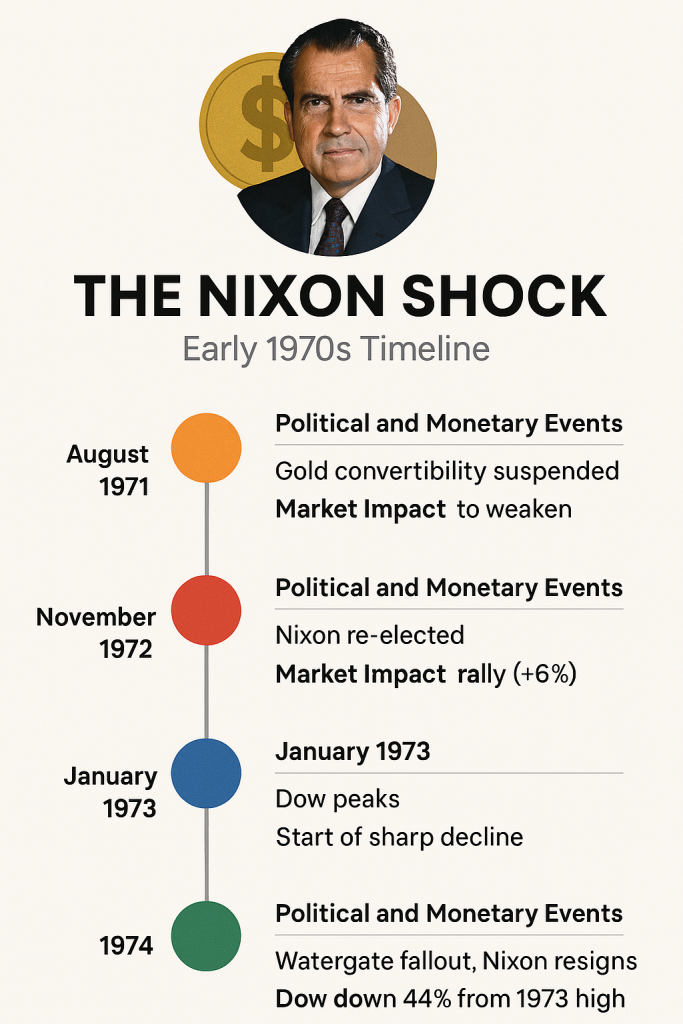
THE NIXON SHOCK — Early 1970’s Timeline
🔶 August 1971 Event: Gold convertibility suspended Market Impact: Dollar begins to weaken Context: Nixon ends Bretton Woods, launching the fiat currency era
🔴 November 1972 Event: Nixon re-elected Market Impact: Stocks rally briefly (+6%) Context: Fed policy remains loose under political pressure
🔵 January 1973 Event: Dow peaks Market Impact: Start of sharp decline Context: Inflation accelerates, investor confidence erodes
🟢 1974 Event: Watergate fallout, Nixon resigns Market Impact: Dow down 44% from 1973 high Context: Recession deepens, Fed credibility damaged.
Current dollar dive, stocks boom and bust (the Dow fell 19% in a year and then by 44% in 1975 from its January 1973 peak). U.S. 10-year Treasury yields surged (peaking at nearly 7.60% -close to twice today’s yield).
In hindsight, Nixon won the election—but lost the economy. And the Fed, caught in the crossfire, paid the price in credibility. It’s a reminder that monetary policy is no place for political theatre.
Is history repeating itself? Is Trump’s involvement different, or another catastrophe waiting to happen?