
‘Err – I meant CLOUD computing!’





The UK is facing a cost of living crisis as inflation has soared to its highest level in decades. The Bank of England has raised interest rates 13 times since December 2021 in an attempt to bring inflation back down to its original target of 2%. But what does this mean for consumers, savers and borrowers?
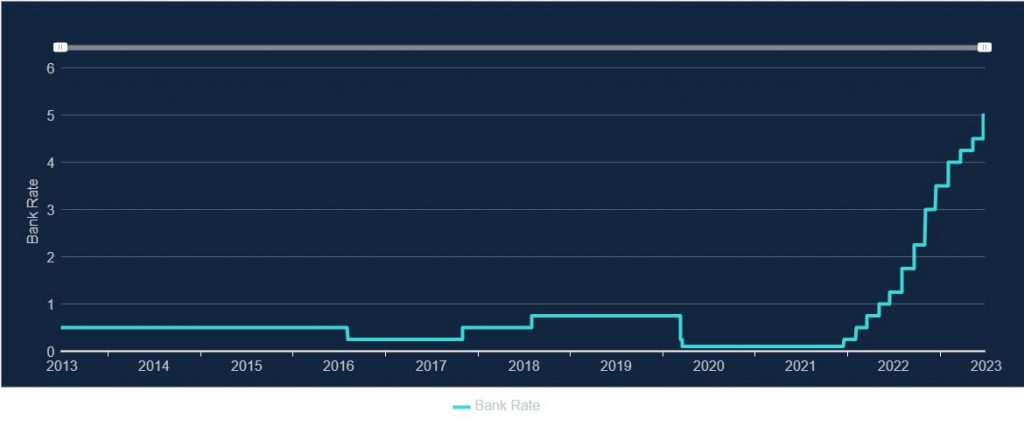
The current UK interest rate is now: 5.0%
Inflation is the term used to describe rising prices. How quickly prices go up is called the rate of inflation. Inflation affects the purchasing power of money, meaning that the same amount of money buys less goods and services over time.
The rate of inflation in the UK is measured by two main indicators: the consumer price index (CPI) and the retail price index (RPI). The CPI is based on a basket of products and services that people typically buy, while the RPI also includes mortgage interest payments.
According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), the CPI inflation rate was 8.7% in the year to May 2023, while the RPI inflation rate was 11.4%. This means that on average, prices were 8.7% and 11.4% higher respectively than they were a year ago.
The main drivers of inflation in the UK are:
Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money or the reward for saving money. The Bank of England sets the bank rate, which is the interest rate it charges to commercial banks that borrow from it. The bank rate influences other interest rates in the economy, such as mortgage rates, loan rates and savings rates.

The Bank of England uses interest rates as a tool to control inflation. The Bank has a target to keep inflation at 2%, but the current rate is more than five times that. When inflation rises, the Bank increases interest rates to make borrowing more expensive and saving more attractive. This reduces the amount of money circulating in the economy and slows down rising prices.
The Bank has raised interest rates 13 times since December 2021, from 0.1% to 5.0%. This is the highest level since March 2009, when interest rates were cut to a record low of 0.5% following the global financial crisis.
Higher inflation means that your money loses value over time. For example, if you had £100 in April 2022 and inflation was 8.7%, you would need £108.70 in April 2023 to buy the same amount of goods and services.
Higher inflation also affects your income, spending, saving and borrowing decisions.
There are some steps you can take to protect your money from inflation, such as:
Inflation and interest rates are two important factors that affect the UK economy and your personal finances. The UK is currently experiencing high inflation due to various factors, such as energy prices, shortages and demand. The Bank of England has raised interest rates to try to bring inflation back down to its target of 2%. Higher inflation and interest rates have implications for your income, spending, saving and borrowing decisions. You can take some steps to protect your money from inflation, such as reviewing your budget, shopping around, paying off debt, saving smartly and investing wisely.
How well has the Bank of England done to keep inflation at or close to 2%?
See next article…
The UK inflation rate remained at 8.7% in the year to May 2023, according to the latest official figures from the Office for National Statistics (ONS). This is the same rate that was recorded in April, but down from the 10.1% level seen in March.
The ONS said that rising prices for air travel, recreational and cultural goods and services, and second-hand cars resulted in the largest upward contributions to the annual inflation rate. However, these were offset by falling prices for motor fuel and food and non-alcoholic beverages.
The ONS also reported that core inflation, which excludes energy, food, alcohol and tobacco, rose to 7.1% in May, up from 6.8% in April, and the highest rate since March 1992.

The inflation rate is measured by the Consumer Prices Index (CPI), which tracks the changes in the cost of a basket of goods and services that are typically purchased by households. The CPIH, which includes owner occupiers’ housing costs, rose by 7.9% in the year to May, up from 7.8% in April.
The high inflation rate has been driven by a combination of factors, including supply chain disruptions, labour shortages, higher energy costs, and strong consumer demand as the economy recovers from the coronavirus pandemic.
The Bank of England has a target to keep inflation at 2%, but it has said that it expects inflation to rise further in the coming months before falling back next year. The Bank has also signalled that it may raise interest rates sooner than expected to curb inflationary pressures.
However, June’s inflation reading came in below economists expectations at 7.3% A small but welcome reversal of high UK inflation. UK inflation is higher than the EU and U.S.
Are central banks doing a good job at controlling inflation? Bear in mind the inflation target is 2%…
This is the Bank Rate set by the Bank of England (BoE), which influences the interest rates that other banks charge borrowers and pay savers. The BoE has raised the Bank Rate 13 times in a row from 0.1% to 5% in a bid to control inflation, which is the rate at which the prices of goods and services increase over time. The BoE has a target of keeping inflation at 2%, but the current inflation rate is 8.7%, which is much higher than the target. This means that the purchasing power of money is decreasing and people have to pay more for the same things.
Promoting the good of the people of the United Kingdom by maintaining monetary and financial stability.

Well, the BoE has clearly done a good job here then with the UK interest rate now at 5%, again… and inflation at 8.7% after peaking at 11.1% in November 2022, a 41 year high! Great job!
And the UK PM said, ‘I always said this would be hard – and clearly it’s got harder over the past few months. I am totally, 100%, on it, and it’s going to be OK‘.
That’s good to know then – it’s going to be OK – so reassuring for borrowers! It’s going to be OK, so don’t worry!
Sorry PM, but that is so weak it’s bordering pathetic. Weren’t you the chancellor too?