China’s humanoid robotics sector has undergone a startling transformation over the past year, shifting from online punchline to global headline.
At the 2026 Spring Festival Gala — the world’s most‑watched television broadcast — a troupe of Chinese-built humanoids delivered a polished sequence of kung fu routines. These were synchronised with dancing skills and acrobatic flips.
A performance that sharply contrasted with their awkward public outings just twelve months earlier.
From failure to back flips – in one year
In early 2025, China’s humanoids were better known for wobbling through folk dances and collapsing mid‑marathon.
Clips of stumbles and system failures circulated widely, fuelling scepticism about whether the country’s robotics ambitions were more hype than substance.
Yet the past year has seen a rapid tightening of engineering, manufacturing and AI integration — and the results are now impossible to ignore.
Analysts note that China’s advantage is structural as much as technical. The country controls a nearly vertically integrated robotics supply chain, from rare earths and high‑performance magnets to batteries and actuators.
Unitree scales up
This ecosystem has enabled companies such as Unitree to scale production at a pace Western rivals struggle to match, while keeping prices dramatically lower.
Unitree’s G1 humanoid, for example, carries a base price of around $13,500, far below the expected near‑term pricing of Tesla’s Optimus platform.
The Gala performance reportedly showcased more than choreography. The robots demonstrated improved dexterity, balance and tool‑handling — capabilities that hint at real industrial potential.
Analysts argue that flips and weapon routines are impressive, but the true economic value lies in tasks requiring fine motor control, endurance and the ability to chain multiple actions together.
These are the areas where humanoids could eventually reshape logistics, manufacturing and even frontline service roles.
Hurdles remain
Still, significant hurdles remain. Reliability in messy, human‑centred environments is far from solved, and the underlying AI models — the systems that allow robots to reason, adapt and plan — remain the decisive battleground.
As one analyst reportedly put it, the robot ‘will only be as useful as its model’, a reminder that physical prowess alone won’t deliver the productivity revolution China hopes for.
Even so, the past year marks a turning point. What was once a source of online mockery has become a showcase of national ambition.
If China maintains its current momentum, the global robotics race may be entering a new, more competitive phase — and this time, the world is paying attention.
Top Chinese Humanoid Robots and What They Do
China’s humanoid robotics industry has exploded in scale and ambition, with hundreds of domestic models now in development or deployment — many designed for real-world tasks, research and emerging commercial use.
These are among China’s most visible humanoids.
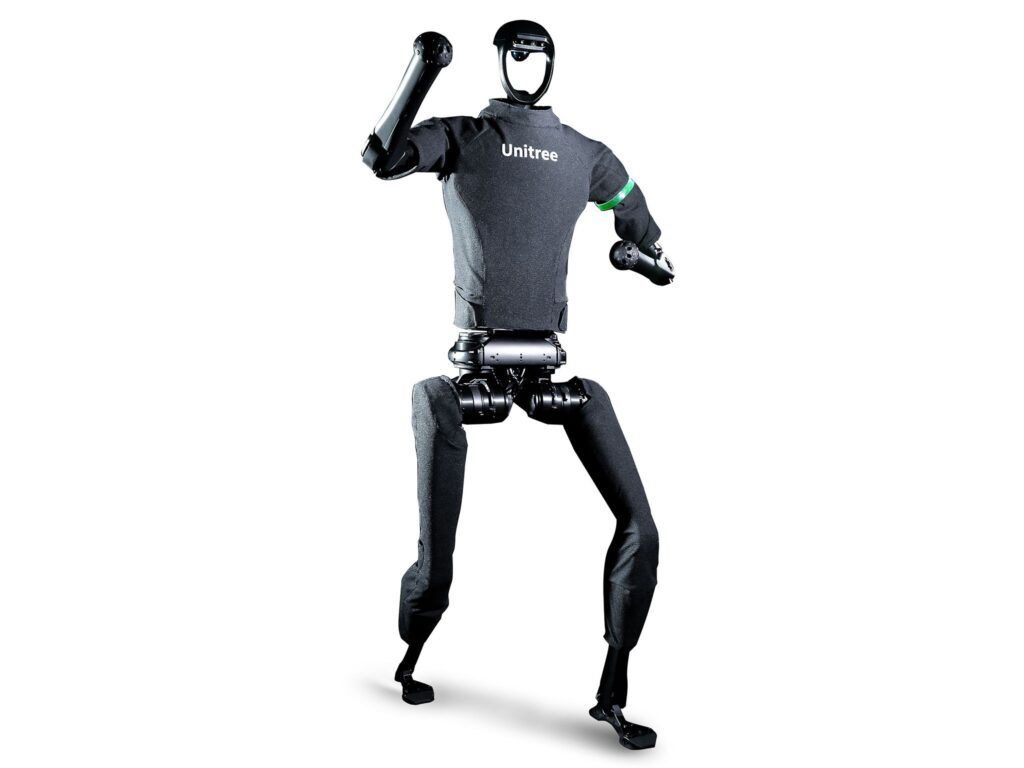
The Unitree G1 is built for agility and athletic performance and was featured in high-profile public displays.
Its advanced motors, balance systems and AI control allow dynamic motion — from kung fu to flips — making it a popular research and entertainment platform.
• Use: demonstrations, research, potential service and logistics applications
• Production goals: Unitree aims to ship up to 20,000 robots in 2026, a dramatic increase from 5,500 in 2025.
2. AgiBot Series
AgiBot has several humanoid designs oriented toward industrial and laboratory tasks, such as vehicle inspections or precision work, using RGB-D cameras and lidar sensors.
• RAISE A1 — tall, capable of 7 km/h walking and heavy lifting
• Yuanzheng A2 — bipedal, sensor-driven for fine manipulation
• Lingxi X1 — open-source design to support wider development
3. Diverse 2026 Models Across Industries
China’s ecosystem now includes many specialised humanoids, each targeting different sectors:
• Dr02 (DEEP Robotics) – industrial-grade, all-weather use
• L7 (Robot Era) – versatile and modular for logistics/research
• Walker S2 (UBTECH) – continuous operation on factory floors
• Forerunner K2 (Kepler Robotics) – precision tasks with advanced sensors
• XMAN-R1 (Keenon Robotics) – service automation and collaborative work
• Stardust Smart S1 (Astribot) – agile and adaptable for commercial interaction
Each of these models shows how far Chinese makers have moved past basic balance and walking, toward real manipulation and decision-making.
Capabilities: From Tools to Interaction
Modern Chinese humanoids are increasingly about practical capability, not just spectacle:
Tool handling
Research and industrial models are designed to grip, carry and operate tools, approaching tasks like part assembly or quality checks in controlled environments.
Sensor integration
Latest designs combine lidar, cameras, IMUs and advanced control software — giving robots robust perception for navigation and object manipulation.
AI and language interaction
Efforts are underway to combine large language models with robot control systems — enabling natural language instructions and more flexible task execution.
Who’s Using Them?
While many humanoids remain in research or industrial contexts today, interest is rising rapidly:
✔️ Research and development labs
✔️ Corporate facilities (testing automation)
✔️ Robotics education and exhibitions
✔️ Early service roles in retail and hospitality
Consumer demand in China has surged since high-visibility events like the Spring Festival Gala, and delivery dates for popular models are being pushed out due to pre-orders.
China’s humanoid robot landscape in 2026 spans high-performance showpieces, industrial task specialists and service-ready platforms.
With thousands of units shipped and ambitious production plans underway, the country is rapidly evolving from prototype demonstrations to tangible real-world deployment.