Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) has posted a record-breaking 39% surge in third-quarter profit, underscoring its pivotal role in the global AI revolution.
The world’s largest contract chipmaker reported net income of NT$452.3 billion (£11.4 billion), far exceeding analyst expectations and marking a new high for the company.
Revenue climbed 30.3% year-on-year to NT$989.92 billion, driven by insatiable demand for high-performance chips powering artificial intelligence applications.
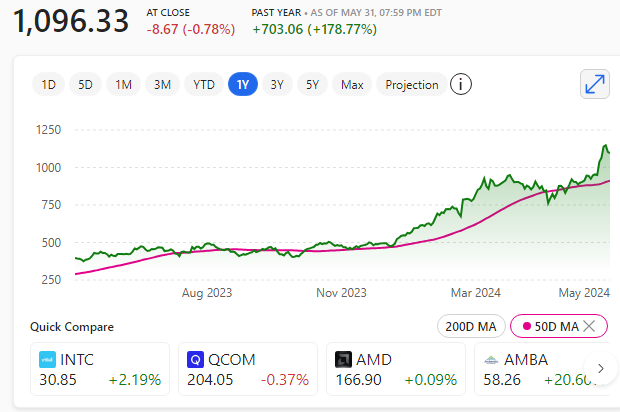
Tech giants including Nvidia, OpenAI, and Oracle have ramped up orders for TSMC’s cutting-edge processors, fuelling the company’s meteoric rise.
TSMC’s CEO, C.C. Wei, reportedly attributed the growth to ‘unprecedented investment in AI infrastructure’, noting that the company’s advanced nodes are now central to training large language models and deploying generative AI tools.
Despite global economic headwinds and ongoing trade tensions, TSMC’s strategic expansion—including a $165 billion global buildout across Arizona, Europe, and Japan—is positioning it as the backbone of next-gen computing.
The results also reflect a broader shift in the semiconductor landscape. As traditional consumer electronics plateau, AI-driven demand is reshaping supply chains and investment priorities.
Analysts suggest that AI chip spending could surpass $1 trillion in the coming years, with TSMC poised to capture a significant share.
For investors and industry observers, the message is clear: AI isn’t just a trend—it’s a fundamental shift. And TSMC, with its unparalleled fabrication expertise and global influence, is quietly shaping the future.
As the AI arms race accelerates, TSMC’s performance offers a glimpse into the future of tech: one where silicon, not software, defines the frontier.
The company’s latest earnings are not just a financial milestone—they’re a signal of where innovation is headed next.