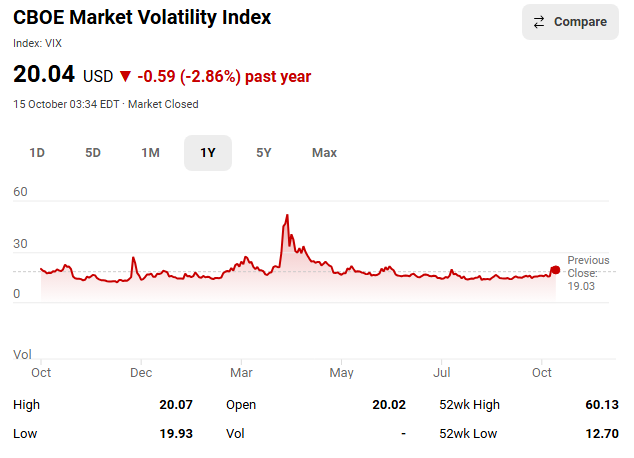
MiniMax’s M2.5 model has emerged as the unexpected frontrunner in China’s latest wave of artificial intelligence releases, earning a clear endorsement from analysts.
While much of the recent global conversation has fixated on DeepSeek’s rapid evolution, China has quietly produced five new frontier‑level models in recent weeks.
Widening choice
Among them—Alibaba’s Qwen 3.5, ByteDance’s Seedance 2.0, Zhipu’s latest offerings, DeepSeek’s V3.2, and MiniMax’s M2.5—it is MiniMax that reportedly has captured institutional attention.
Some analysts reportedly cite its performance, pricing, and commercial readiness as the reasons it stands apart.
MiniMax, which listed publicly in Hong Kong in January, released M2.5 in mid‑February 2026. The model rivals Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.6 in capability while costing a fraction of the price—an advantage that has driven a surge of developer adoption.
Data from OpenRouter reportedly shows developers increasingly choosing M2.5 over DeepSeek’s V3.2 and even several U.S. based models.
Analysts argue that this combination of competitive performance and aggressive pricing positions MiniMax as the Chinese model with the strongest global commercial potential.
Productive and less expensive
The model’s technical profile reinforces that view. M2.5 is designed for real‑world productivity, with strengths in coding, agentic tool use, search, and office workflows.
It reportedly scores around 80.2% on SWE‑Bench Verified and outperforms leading Western models—including Claude Opus 4.6, GPT‑5.2, and Gemini 3 Pro—on tasks involving web search and office automation, all while operating at ten to twenty times lower cost.
MiniMax describes the model as delivering “intelligence too cheap to meter,” a claim supported by its lightweight Lightning variant, which generates 100 tokens per second and can run continuously for an hour at roughly one dollar.
This shift signals a broader trend: China’s AI race is no longer defined by a single breakout model. Instead, a competitive ecosystem is emerging, with MiniMax demonstrating that cost‑efficient frontier performance can reshape developer behaviour and enterprise planning.
For global markets, UBS’s preference suggests that investors are beginning to look beyond headline‑grabbing releases and toward models with sustainable commercial trajectories.
Comparison of China’s Five New AI Models
| Model | Developer | Key Strengths | Performance Notes | Pricing Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiniMax M2.5 | MiniMax | Coding, agentic tasks, office automation | Rivals Claude Opus 4.6; 80.2% SWE‑Bench Verified; outperforms GPT‑5.2 and Gemini 3 Pro on search/office tasks | Extremely low cost; “too cheap to meter” |
| DeepSeek V3.2 | DeepSeek | Reasoning, general chat | Strong but losing developer share to M2.5 | Low‑cost but not as aggressive as MiniMax |
| Alibaba Qwen 3.5 | Alibaba | Enterprise integration, multilingual capability | Part of Alibaba’s expanding Qwen family | Competitive mid‑range |
| ByteDance Seedance 2.0 | ByteDance | Video generation | Focused on multimodal creativity | Premium creative‑tool pricing |
| Zhipu (latest models) | Zhipu AI | Knowledge tasks, enterprise AI | Continues Zhipu’s push into LLM infrastructure | Mid‑range enterprise |
MiniMax M2.5 leads China’s AI surge with performance rivalling Claude Opus and Gemini 1.5 Pro, yet at a fraction of the cost.

It excels in coding, search, and office automation, scoring 80.2% on SWE‑Bench Verified. DeepSeek V3.2 offers strong reasoning but lags in developer adoption.
Qwen 3.5 and Zhipu target enterprise AI, while ByteDance’s Seedance 2.0 focuses on video generation.
Compared to ChatGPT-4, Claude 2.1, and Gemini 1.5, China’s models are closing the gap in capability, with MiniMax M2.5 now outperforming Western leaders on several benchmarks—especially in speed and cost efficiency.
Comparison of leading Chinese and Western AI models
(SWE‑Bench Verified — latest public leaderboard, early 2026) guide data
| Model | Developer | Primary Strengths | SWE‑Bench Verified | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claude 4.6 Opus | Anthropic | High‑end reasoning, long‑context reliability | 76–77% | Current top performer on independent coding benchmarks. |
| Gemini 3 Flash | Google DeepMind | Fast reasoning, efficient tool use | ~75–76% | Extremely strong structured reasoning. |
| MiniMax M2.5 | MiniMax | Coding, agentic tasks, office automation | 75–76% (independent) / 80.2% (internal) | Strongest Chinese model with published results. |
| GPT‑4o (used in ChatGPT\)* | OpenAI | Multimodal, real‑time interaction, broad generalist | ~72–74% | \*ChatGPT is a product wrapper; GPT‑4o is the underlying model used for benchmarking. |
| Gemini 3 Pro Preview | Google DeepMind | Multimodal, search, office tools | ~74% | Strong generalist. |
| DeepSeek V3.2 | DeepSeek | Reasoning, general chat | No independent SWE‑Bench score | Not on the verified leaderboard. |
| Alibaba Qwen 3.5 | Alibaba | Enterprise integration, multilingual | No independent SWE‑Bench score | Not included in latest run. |
| Zhipu GLM‑5 | Zhipu AI | Knowledge tasks, enterprise AI | No independent SWE‑Bench score | Awaiting verified results. |
| Seedance 2.0 | ByteDance | Video generation | N/A | Not a coding model. |
*Note:
- “ChatGPT” is not a single model and cannot be benchmarked.
- GPT‑4o is the model that powers ChatGPT for most users, so it is the correct entry for comparison.
Comparison
- Claude 4.6 Opus is the current top performer on independently verified coding tasks.
- MiniMax M2.5 is the strongest Chinese model with published independent results and is now competitive with the best Western models.
- DeepSeek, Qwen, and Zhipu have not yet been evaluated on the latest independent SWE‑Bench Verified run, so they cannot be directly compared.
- Seedance 2.0 remains a video model and is not part of coding benchmarks.
- Token speeds are intentionally excluded because no vendor publishes standardised, reproducible numbers.
Tables and data provided for indication of AI model status (provided as a guide only).