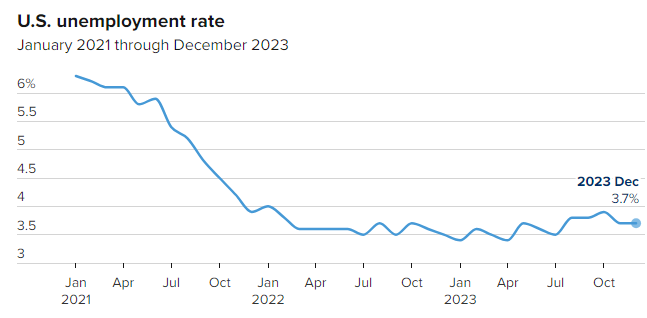
In September 2024, the U.S. economy saw a significant increase in job additions, substantially surpassing expectations and contributing to a robust employment landscape as the unemployment rate declined, according to the U.S. Labor Department’s report issues Friday 4th October 2024.
U.S. Non-farm payroll numbers rose by 254,000 in September 2024, a jump from the revised figure of 159,000 in August and exceeding the forecast of 150,000.
The unemployment rate dropped to 4.1%, a decrease of 0.1 percentage point, while the household employment survey reported a substantial increase of 430,000 jobs.
Average hourly earnings grew by 0.4% for the month and saw a 4% rise compared to the previous year, outpacing the projected estimates.