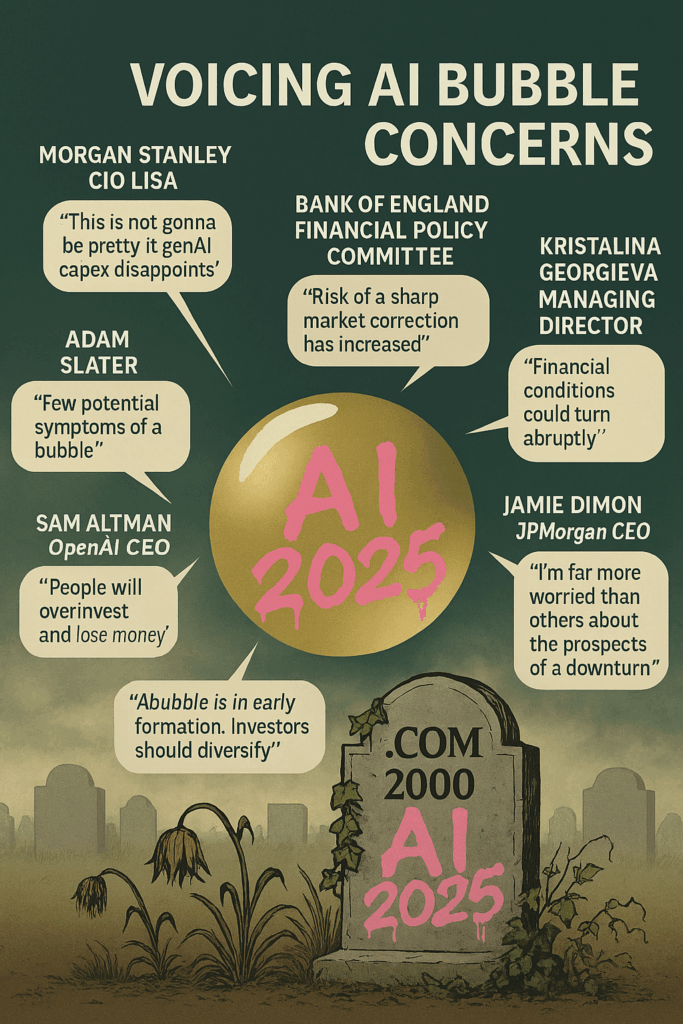
When artificial intelligence first ignited investor enthusiasm, it lifted almost every major technology stock.
The narrative was simple: AI would transform industries, boost productivity and unlock vast new revenue streams.
Yet as the cycle matures, markets are becoming more selective. In recent weeks, shares of IBM have drifted lower, illustrating how the ‘AI effect’ can cut both ways.
At first glance, IBM should be a prime beneficiary. The company has spent years repositioning itself around hybrid cloud infrastructure, data analytics and enterprise AI solutions.
Its Watson platform has been refreshed with generative AI tools designed to automate customer service, streamline software development and enhance business decision-making. Management has repeatedly emphasised AI as a core growth engine.
Market Expectations
However, the market’s expectations have shifted. Investors are increasingly rewarding companies that sit at the very heart of AI infrastructure — those supplying advanced semiconductors, high-performance computing capacity and hyperscale cloud services.
These businesses are reporting visible surges in AI-related demand, often accompanied by sharp revenue acceleration and expanding margins.
By contrast, IBM’s AI exposure is embedded within broader consulting and software operations, making its growth trajectory appear steadier rather than explosive.
This distinction matters in a momentum-driven environment. When earnings updates fail to deliver dramatic upside surprises, shares can quickly lose favour.
Less AI Effect
IBM’s results have shown progress in software and recurring revenue, but they have not reflected the kind of dramatic AI-driven uplift seen elsewhere in the sector. For some investors, that raises questions about competitive positioning and pricing power.
There is also a perception issue. Despite its reinvention efforts, IBM still carries the legacy image of a mature technology conglomerate rather than a cutting-edge AI disruptor.
In a market captivated by bold innovation stories, narrative can influence valuation just as much as fundamentals.
If capital flows concentrate in a handful of high-growth AI names, diversified players may struggle to keep pace in share price performance.
AI Tension
Yet the sell-off may also highlight a deeper tension within the AI theme. Enterprise adoption of AI tools tends to be gradual, cautious and closely tied to measurable productivity gains.
IBM’s strategy is built around long-term integration rather than short-term hype. While that approach may lack immediate fireworks, it could prove more durable as corporate clients prioritise reliability, governance and cost control.
For now, though, the AI effect is amplifying investor discrimination. In a market eager for rapid transformation, IBM’s more measured path has translated into weaker share performance — a reminder that not all AI exposure is valued equally.
Further discussion
IBM has found itself on the wrong side of the artificial intelligence boom, with its shares tumbling more than 13% after Anthropic unveiled a new capability that directly targets one of the company’s most enduring revenue pillars: COBOL modernisation.
The sell‑off reflects a broader market anxiety that AI is beginning to erode long‑protected niches in enterprise technology, and IBM has become the latest high‑profile casualty.
For decades, IBM has been synonymous with mainframe computing and the maintenance of vast COBOL‑based systems that underpin global finance, government services, airlines, and retail transactions.
These systems are notoriously complex, expensive to update, and dependent on a shrinking pool of specialist developers.
Premium Brand
That scarcity has long worked in IBM’s favour, allowing it to charge a premium for modernisation and support.
Anthropic’s announcement threatens to upend that equation. Its Claude Code tool, the company claims, can automate the most time‑consuming and costly parts of understanding and restructuring legacy COBOL environments.
Tasks that once required teams of analysts months to complete—mapping dependencies, documenting workflows, identifying risks—can now be accelerated dramatically through AI‑driven analysis.
The implication is clear: modernising legacy systems may no longer require the same level of human expertise, nor the same level of spending.
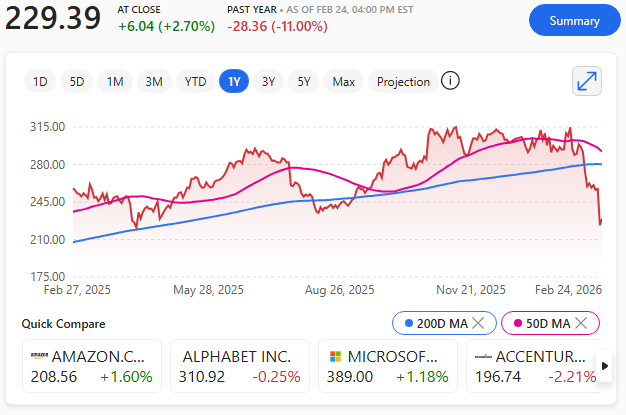
Investors reacted swiftly. IBM’s share price fell to $223.35, extending a year‑to‑date decline of more than 24% – recovering later to $229.39
The drop reflects not only concerns about lost revenue, but also the fear that IBM’s competitive moat—built on decades of institutional reliance on COBOL—may be eroding faster than expected.
The timing has amplified market jitters. Only days earlier, cybersecurity stocks were hit by another Anthropic announcement: Claude Code Security, a feature designed to scan codebases for vulnerabilities.
AI Mood Logic
The rapid expansion of AI into specialised technical domains has created a ‘sell first, ask questions later’ mood across the market, with investors increasingly wary of companies whose business models depend on labour‑intensive or legacy‑bound processes.
For IBM, the challenge now is to demonstrate that it can harness AI rather than be displaced by it.
The company has invested heavily in its own AI initiatives, but the latest market reaction suggests investors are unconvinced that these efforts will offset the threat to its traditional strongholds.
The AI revolution is reshaping the technology landscape at speed. IBM’s sharp decline is a reminder that even the industry’s oldest giants are not insulated from disruption—and that the next wave of AI competition may hit the most established players hardest.
But remember, this is IBM we are talking about.
Explainer
What is COBOL?
COBOL is an old but remarkably durable programming language created in the late 1950s to run business, finance, and government systems, and it’s still powering much of the world’s banking and administrative infrastructure today.
It was designed to read almost like plain English, making it easier for non‑technical managers to understand, and its stability means many core systems have never been replaced.